The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve or Cranial Nerve VI, plays a vital role in controlling eye movement. It is responsible for the lateral movement of the eye, allowing us to look from side to side. Understanding the anatomy, function, and disorders related to the abducens nerve can provide valuable insights into various eye-related conditions. In this article, we will explore the pathway of the abducens nerve, its entry into the orbit, and its significance in the medical field.
Understanding the Abducens Nerve
Anatomy of the Abducens Nerve
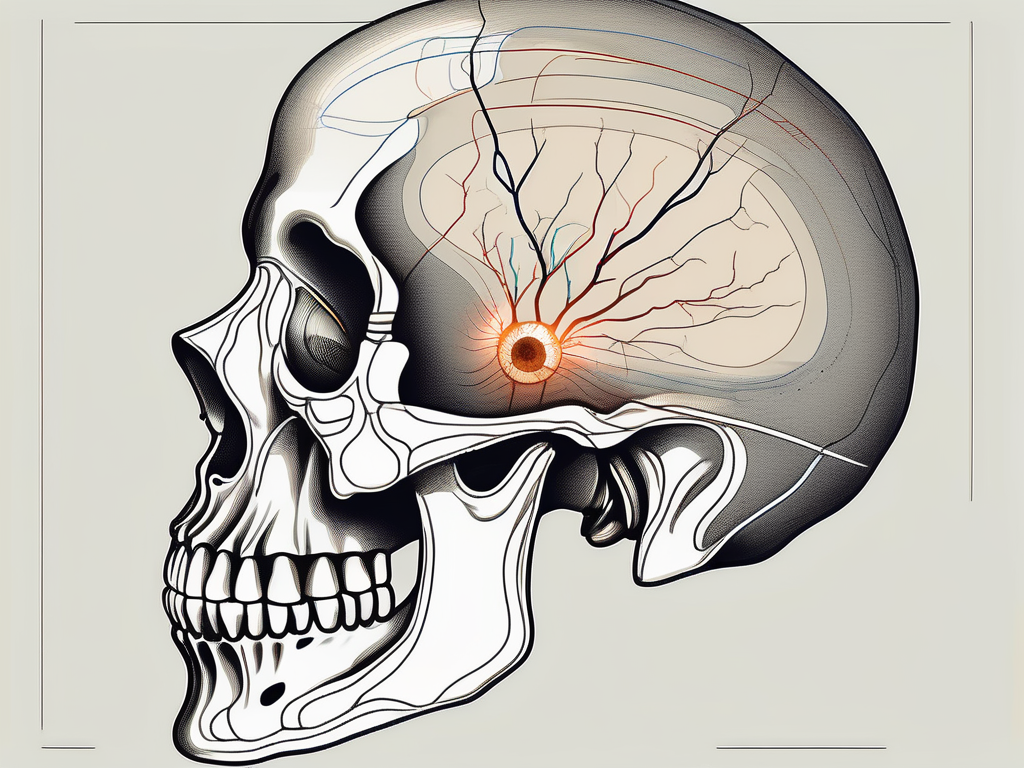
The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in controlling eye movement. It arises from the lower part of the pons, a region in the brainstem responsible for relaying signals between the brain and the body. As it emerges, the abducens nerve takes the form of a small rootlet, delicately traversing through the subarachnoid space, a fluid-filled area that surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
As the abducens nerve continues its journey, it enters the cavernous sinus, a venous structure located behind the eye. This sinus serves as a pathway for various structures, including blood vessels and nerves, to travel to and from the brain. Within the cavernous sinus, the abducens nerve weaves its way, navigating the intricate network of structures, until it reaches its next destination.
After its passage through the cavernous sinus, the abducens nerve reaches the superior orbital fissure, an opening in the bony orbit that leads to the eye socket. This fissure, situated between the sphenoid bone and the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, serves as a gateway for the abducens nerve to enter the orbit and carry out its important functions.
Once inside the orbit, the abducens nerve follows a specific course to reach its target muscles. It travels along the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus, delicately navigating through the complex anatomy of the orbit. Its ultimate destination is the lateral rectus muscle, one of the six extraocular muscles responsible for controlling eye movements.
Function of the Abducens Nerve
The abducens nerve plays a vital role in coordinating eye movements and ensuring visual stability. Its main function is to innervate the lateral rectus muscle, which is responsible for moving the eye laterally, away from the midline of the body. When the abducens nerve is activated, it signals the lateral rectus muscle to contract, resulting in abduction of the eye.
This action allows us to focus on objects from different angles and maintain proper alignment of both eyes. The abducens nerve works in harmony with other cranial nerves and extraocular muscles to ensure smooth and coordinated eye movements, enabling us to explore our surroundings and engage with the world around us.
Understanding the intricate anatomy and function of the abducens nerve provides valuable insight into the complex mechanisms that govern our ability to see and perceive the world. The delicate interplay between the brain, nerves, and muscles highlights the remarkable precision and coordination required for even the simplest of eye movements.
The Pathway of the Abducens Nerve
Origin and Course of the Abducens Nerve
As mentioned earlier, the abducens nerve originates from the pons, a region located in the brainstem. It arises from the nucleus of the abducens nerve, which is responsible for generating impulses that control movement of the lateral rectus muscle. From its origin, the abducens nerve takes a course that leads it towards the orbit.
The abducens nerve, also known as cranial nerve VI, is a vital component of the intricate network of nerves that control eye movement. Its origin in the pons highlights its significance in coordinating the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, which is responsible for outward gaze. This muscle plays a crucial role in allowing us to shift our focus from one object to another, facilitating smooth eye movements.
Traversing through the brainstem, the abducens nerve embarks on a fascinating journey. It travels through the subarachnoid space, a fluid-filled cavity surrounding the brain, before entering the cavernous sinus. This pathway is not only a physical route for the nerve but also a testament to the remarkable complexity of our anatomy.
The subarachnoid space, filled with cerebrospinal fluid, acts as a protective cushion for the brain. It provides a conduit for the abducens nerve, allowing it to navigate through the intricate web of neural structures. As the nerve makes its way through this space, it encounters various other cranial nerves and blood vessels, forming connections that are crucial for the proper functioning of our visual system.
Upon entering the cavernous sinus, the abducens nerve finds itself in the company of other cranial nerves and vascular structures. This sinus, a complex network of veins located on both sides of the sella turcica, adds another layer of intricacy to the path of the abducens nerve. The close proximity of these structures emphasizes the interdependence and interconnectedness of our bodily systems.
The Abducens Nerve and the Brainstem
The brainstem, comprising the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata, is a vital region responsible for controlling various essential functions of the body. The abducens nerve, originating from the pons within the brainstem, plays a pivotal role in eye movement. This connection highlights the intricate relationship between the abducens nerve and the brainstem, underscoring the need for caution when dealing with conditions that affect the abducens nerve.
Disorders or injuries that impact the abducens nerve can have far-reaching consequences beyond eye movement. The brainstem, being the control center for vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure regulation, relies on the proper functioning of all its components, including the abducens nerve. Any disruption to this delicate balance can potentially affect these crucial bodily functions, emphasizing the importance of understanding the intricate connections within our neural architecture.
Studying the pathway of the abducens nerve not only sheds light on the mechanics of eye movement but also serves as a reminder of the remarkable complexity of our anatomy. The intricate interplay between the abducens nerve, the brainstem, and other cranial nerves showcases the intricacy and interconnectedness of our bodily systems, highlighting the awe-inspiring nature of the human body.
The Abducens Nerve and the Orbit
Entry Point of the Abducens Nerve into the Orbit
Once the abducens nerve traverses the cavernous sinus, it enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure. This fissure is an anatomical opening located between the greater and lesser wings of the sphenoid bone. Its role is to provide a pathway for multiple structures, including nerves, blood vessels, and extraocular muscles, in and out of the orbit.
As the abducens nerve enters the orbit, it continues its path towards the lateral rectus muscle, which it innervates. The ability of the abducens nerve to precisely control the movement of the lateral rectus muscle allows for coordinated lateral eye movements and contributes to our binocular vision.
The superior orbital fissure not only serves as a gateway for the abducens nerve but also accommodates other important structures. The ophthalmic vein, which drains blood from the orbit, passes through this opening. Additionally, the frontal nerve, a branch of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve, enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure. This nerve provides sensory innervation to the forehead and scalp.
Furthermore, the superior orbital fissure allows for the passage of the trochlear nerve, which innervates the superior oblique muscle. This muscle plays a crucial role in eye movements, particularly in downward and inward rotations. The coordinated action of the abducens nerve, innervating the lateral rectus muscle, and the trochlear nerve, innervating the superior oblique muscle, ensures smooth and precise eye movements in various directions.
Role of the Abducens Nerve in Eye Movement
The abducens nerve plays a crucial role in controlling eye movement. Upon activation, impulses generated by the abducens nerve cause the lateral rectus muscle to contract. This contraction results in the abduction of the eye, allowing it to move away from the midline. These lateral eye movements are vital for visually tracking objects and maintaining normal eye alignment.
Eye movements are complex and involve the coordinated action of multiple cranial nerves and extraocular muscles. The abducens nerve works in conjunction with the oculomotor nerve, which innervates most of the other extraocular muscles, to ensure precise and synchronized eye movements. This intricate network of nerves and muscles allows us to perform tasks such as reading, driving, and following moving objects with ease.
In addition to its role in lateral eye movements, the abducens nerve also contributes to the convergence reflex. When we focus on a nearby object, the eyes must turn inward to maintain binocular vision. The abducens nerve plays a part in this process by relaxing the lateral rectus muscle on the side of the eye that is turning inward, allowing the medial rectus muscle to contract and bring the eyes closer together.
Disorders affecting the abducens nerve can lead to various eye movement abnormalities. For example, damage to the abducens nerve can result in a condition known as abducens nerve palsy, characterized by the inability to abduct the affected eye. This can cause double vision, difficulty with lateral gaze, and a misalignment of the eyes, known as strabismus.
In conclusion, the abducens nerve is a vital component of the intricate system that controls eye movements. Its entry into the orbit through the superior orbital fissure allows it to innervate the lateral rectus muscle, contributing to coordinated lateral eye movements. Understanding the anatomy and function of the abducens nerve is crucial in diagnosing and managing conditions that affect eye movements and maintaining optimal visual function.
Disorders Related to the Abducens Nerve
The abducens nerve is a crucial component of the cranial nerves responsible for controlling eye movement. When this nerve is affected by dysfunction or damage, it can lead to a condition known as abducens nerve palsy. This condition impairs the ability to move the eye laterally, resulting in a horizontal gaze palsy.
One of the most common symptoms experienced by individuals with abducens nerve palsy is the inability to move their eyes laterally. This limitation can significantly impact their daily activities, making tasks such as reading, driving, or even watching television challenging. Additionally, double vision, eye misalignment, and difficulty focusing on objects in the lateral field of vision are also common symptoms.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. A thorough evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional, such as an ophthalmologist or a neurologist, is essential to determine the underlying cause of the abducens nerve palsy and guide appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Abducens Nerve Disorders
The treatment of abducens nerve disorders depends on various factors, including the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In some cases, the underlying cause may be reversible, and treatment focuses on addressing the root cause. For instance, if abducens nerve palsy is secondary to trauma, conservative management and monitoring may be recommended, allowing the nerve time to heal.
However, in more severe cases or when the underlying cause is not reversible, additional treatment options may be necessary. One such option is the use of prism glasses, which can help correct double vision and improve visual function. These specialized glasses work by redirecting light to compensate for the misalignment of the eyes, allowing for clearer and more comfortable vision.
Another treatment approach for abducens nerve disorders is eye patching. This technique involves covering one eye with a patch to alleviate symptoms such as double vision and eye misalignment. By blocking the vision in one eye, the brain can focus on the images from the unaffected eye, reducing visual disturbances and improving overall visual perception.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to address the underlying issue and alleviate symptoms. Strabismus surgery, a common surgical procedure for abducens nerve disorders, aims to improve eye alignment and enhance visual function. During this procedure, the eye muscles are adjusted to correct misalignment and restore normal eye movement. Surgical intervention can provide long-term relief for individuals with severe abducens nerve disorders.
In conclusion, abducens nerve disorders can significantly impact an individual’s ability to move their eyes laterally and can cause various visual disturbances. Seeking prompt medical attention and a thorough evaluation is crucial for determining the underlying cause and guiding appropriate treatment. Treatment options range from conservative management and monitoring to the use of prism glasses, eye patching, or surgical interventions such as strabismus surgery. With the right treatment approach, individuals with abducens nerve disorders can experience improved eye movement, enhanced visual function, and a better quality of life.
The Abducens Nerve in the Medical Field
The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, plays a vital role in eye movement. It innervates the lateral rectus muscle, which is responsible for moving the eye outward. Dysfunction of the abducens nerve can lead to a condition called abducens nerve palsy, causing a range of symptoms such as double vision, difficulty moving the affected eye, and eye misalignment.
Diagnostic Procedures Involving the Abducens Nerve
Various diagnostic procedures can help assess the function and integrity of the abducens nerve. Ophthalmic examinations are commonly performed to evaluate eye movement and alignment. These examinations may include tests such as the Hirschberg test, which involves shining a light into the eyes to assess the position of the corneal reflection.
Neuroimaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, can provide detailed images of the brain and cranial nerves. These imaging techniques are particularly useful in identifying any structural abnormalities or lesions that may be affecting the abducens nerve.
Electrophysiological tests, such as electrooculography (EOG) or electromyography (EMG), can measure the electrical activity of the muscles involved in eye movement. These tests can help determine the extent of nerve damage and provide valuable information for treatment planning.
Additionally, a careful medical history and comprehensive neurological assessment are crucial in identifying any underlying conditions contributing to abducens nerve dysfunction. Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, trauma, or tumors can all affect the function of the abducens nerve. Proper evaluation and accurate diagnosis are essential for appropriate management and treatment recommendations.
Surgical Considerations for the Abducens Nerve
In certain cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address specific conditions affecting the abducens nerve. Surgical considerations revolve around the underlying cause and location of the nerve dysfunction. For example, if the abducens nerve is compressed by a tumor or aneurysm, surgical removal or decompression may be required to relieve the pressure on the nerve.
The expertise of neurosurgeons, ophthalmologists, and other healthcare professionals is crucial in planning and performing surgical procedures to optimize outcomes and minimize potential complications. These specialists work together to develop a personalized treatment plan based on the individual’s specific condition and needs.
It is important to remember that every case is unique, and treatment decisions should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional. They will consider factors such as an individual’s medical history, overall health status, and the specific circumstances surrounding the abducens nerve disorder. Treatment options may include conservative management, medication, physical therapy, or surgical intervention, depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the abducens nerve, with its intricate pathway and key role in controlling eye movement, holds great significance in the human body. An understanding of the anatomy, function, and disorders associated with the abducens nerve helps shed light on eye-related conditions and guides appropriate management strategies.
If you experience any symptoms related to the abducens nerve or have concerns about your eye health, it is crucial to seek medical advice. A qualified healthcare professional can provide a thorough evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and individualized treatment plan based on your specific needs and circumstances.
Leave a Reply