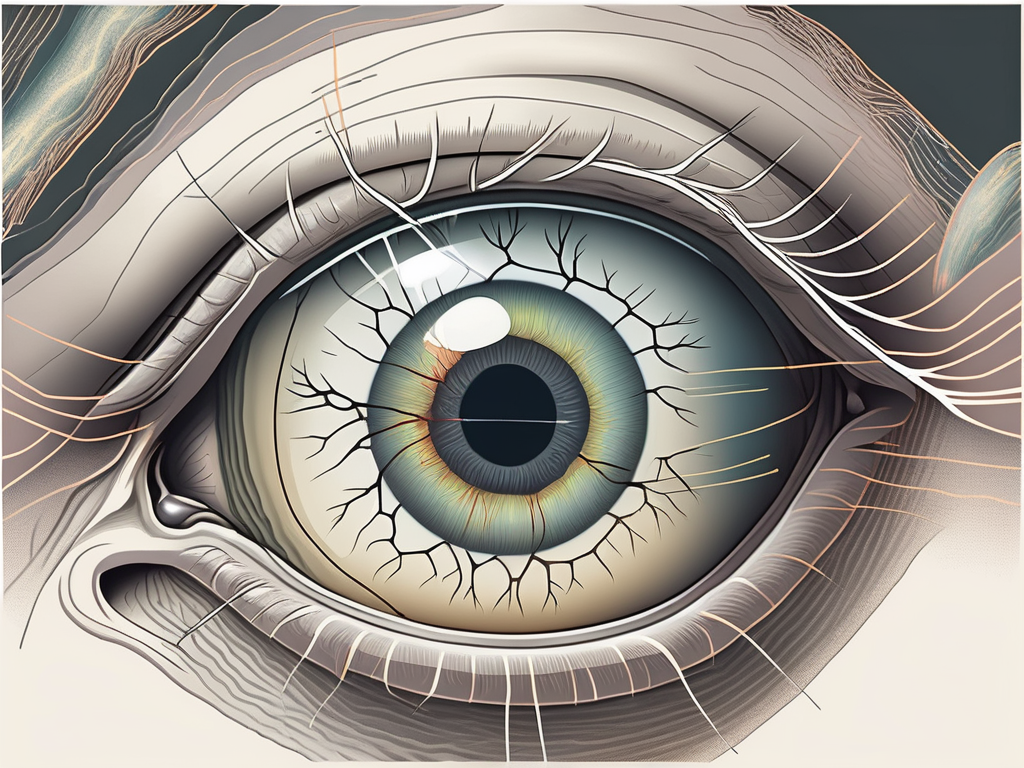
The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in controlling eye movements. It specifically innervates the lateral rectus muscle, which is one of the six extrinsic eye muscles. The lateral rectus muscle is responsible for abducting or moving the eye laterally away from the midline of the body.
Understanding the Abducens Nerve
In order to grasp the significance of the abducens nerve and its relationship with the extrinsic eye muscles, it is essential to delve into the anatomy and function of this vital cranial nerve.
The abducens nerve, also known as cranial nerve VI, plays a crucial role in eye movement and coordination. It is responsible for controlling the lateral rectus muscle, which allows the eye to move away from the midline of the body. This movement, known as abduction, is essential for directing our gaze towards objects located laterally.
Anatomy of the Abducens Nerve
The abducens nerve originates from the brainstem, specifically the pons region, and emerges from the cranial cavity through the superior orbital fissure to enter the orbit. It then travels alongside the other cranial nerves, navigating its way to the lateral rectus muscle.
Within the brainstem, the abducens nerve fibers originate from the abducens nucleus, which is located in the pons portion. These motor fibers extend from the nucleus and form the abducens nerve, creating a pathway for nerve signals to reach the lateral rectus muscle.
The abducens nerve consists of motor fibers that control muscle movement, making it a purely motor nerve. These fibers carry signals from the brainstem to the lateral rectus muscle, allowing it to contract and move the eye laterally.
Function of the Abducens Nerve
The primary function of the abducens nerve is to control the lateral rectus muscle, enabling it to abduct the eye. This movement is crucial in allowing us to direct our gaze to objects located laterally.
Eye movements are complex and require the coordination of multiple cranial nerves and extraocular muscles. The abducens nerve works in conjunction with other cranial nerves, such as the oculomotor nerve (cranial nerve III) and the trochlear nerve (cranial nerve IV), to ensure smooth and accurate eye movements.
When the abducens nerve is functioning properly, it sends signals to the lateral rectus muscle, causing it to contract and move the eye laterally. This coordinated movement allows us to explore our visual environment and focus on objects of interest.
However, dysfunction or damage to the abducens nerve can result in a condition known as abducens nerve palsy. This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms, including difficulty in moving the affected eye laterally, double vision, and misalignment of the eyes.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the abducens nerve is crucial for healthcare professionals, as it helps in diagnosing and treating conditions related to eye movement disorders. By comprehending the intricate interactions between the abducens nerve, other cranial nerves, and the extraocular muscles, medical professionals can provide appropriate interventions to improve eye movements and restore visual function.
The Extrinsic Eye Muscles
Before we explore the connection between the abducens nerve and the extrinsic eye muscles, it is important to familiarize ourselves with the overall role and function of these muscles.
Overview of Extrinsic Eye Muscles
The extrinsic eye muscles, also referred to as the extraocular muscles, are a group of six muscles that surround each eye. These muscles work collaboratively to control the precise movements of the eye in multiple directions.
Let’s dive deeper into each of these muscles:
The medial rectus muscle is responsible for inward eye movements, allowing us to look towards our nose. This muscle is innervated by the oculomotor nerve.
The superior rectus muscle helps in upward eye movements, allowing us to look towards the sky. It is also innervated by the oculomotor nerve.
The inferior rectus muscle aids in downward eye movements, allowing us to look towards the ground. Like the superior rectus muscle, it is innervated by the oculomotor nerve.
The superior oblique muscle plays a crucial role in rotating the eye downward and away from the midline. It is innervated by the trochlear nerve.
The inferior oblique muscle is responsible for rotating the eye upward and away from the midline. It is innervated by the oculomotor nerve.
Lastly, the lateral rectus muscle, which we mentioned earlier, is innervated by the abducens nerve. It controls the outward movement of the eye, allowing us to look towards the side.
Role of Extrinsic Eye Muscles in Vision
The intricate teamwork between the extrinsic eye muscles is essential for our ability to see clearly and to adapt our gaze in response to visual stimuli. The collective function of these muscles allows us to focus on objects at various distances, track moving objects, and maintain binocular vision.
For example, when we read a book, our eyes move smoothly across the page due to the coordinated efforts of the extrinsic eye muscles. These muscles ensure that our eyes are aligned and that we can accurately follow the text.
Furthermore, the extrinsic eye muscles enable us to have depth perception. By converging our eyes, the muscles help us perceive the distance between objects in our visual field. This is crucial for activities such as catching a ball or judging the distance of an approaching car.
Without the coordinated movement of the extrinsic eye muscles, our ability to carry out even the simplest visual tasks would be severely compromised.
The Connection Between the Abducens Nerve and Extrinsic Eye Muscles
Now that we have explored the individual significance of the abducens nerve and extrinsic eye muscles, let’s delve deeper into their vital connection and how they work together to enable precise eye movements.
The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in controlling eye movement. When the abducens nerve is functioning optimally, it sends motor signals to the lateral rectus muscle, causing it to contract. This contraction results in the lateral movement of the eye, aiding in the visual tracking of objects located laterally.
However, it is important to note that the abducens nerve does not act alone in controlling eye movements. It harmonizes its function with the other cranial nerves and extrinsic eye muscles, allowing for coordinated eye movements in multiple directions.
Among the six extrinsic eye muscles, the abducens nerve has a crucial role in innervating the lateral rectus muscle. This direct connection ensures that the lateral rectus muscle can carry out its essential function of abducting the eye and maintaining visual alignment during horizontal movements.
Now, let’s explore the intricate coordination between the abducens nerve and the other cranial nerves involved in eye movement. The abducens nerve works in harmony with the oculomotor nerve, which innervates the remaining five extrinsic eye muscles. Together, these two nerves ensure smooth and precise eye movements in all directions.
When the abducens nerve sends signals to the lateral rectus muscle, the oculomotor nerve simultaneously sends signals to the remaining four rectus muscles (superior, inferior, medial). This coordinated effort allows for vertical and diagonal eye movements, complementing the lateral movement controlled by the abducens nerve.
Furthermore, the trochlear nerve, another cranial nerve, innervates the superior oblique muscle. This muscle plays a crucial role in rotating the eye downward and inward. The abducens nerve and the trochlear nerve work together to ensure accurate and coordinated eye movements, allowing us to navigate the world around us with precision.
It is fascinating to consider the intricate network of nerves and muscles involved in eye movement. The abducens nerve, with its connection to the lateral rectus muscle, is just one piece of this complex puzzle. Together, these components work seamlessly to enable us to focus on objects of interest, track moving targets, and explore our visual environment.
Disorders Related to the Abducens Nerve and Extrinsic Eye Muscles
Despite their vital roles, the abducens nerve and extrinsic eye muscles can be subject to various disorders that can impact eye movements and visual function. It is important to be aware of these disorders and their potential symptoms.
The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in controlling the lateral movement of the eye. It innervates the lateral rectus muscle, which is responsible for abducting the eye, allowing it to move away from the midline. The coordinated action of the abducens nerve and the extrinsic eye muscles is essential for proper eye alignment and binocular vision.
Disorders affecting the abducens nerve and extrinsic eye muscles can result from various causes, including trauma, infections, inflammation, tumors, vascular disorders, and neurological conditions. These disorders can disrupt the normal functioning of the nerve and muscles, leading to a range of symptoms that can significantly impact visual function.
Symptoms of Abducens Nerve Palsy
Abducens nerve palsy, also known as sixth nerve palsy, occurs when there is damage or dysfunction to the abducens nerve. This condition can result in the inability to abduct the affected eye, leading to double vision, reduced eye movements, and difficulty focusing on objects located laterally.
Double vision, also known as diplopia, is a common symptom of abducens nerve palsy. This occurs because the affected eye is unable to move laterally, causing misalignment with the other eye. As a result, the brain receives conflicting visual information from each eye, leading to the perception of two separate images.
In addition to double vision, individuals with abducens nerve palsy may experience reduced eye movements, especially when attempting to look towards the affected side. This limitation in eye movement can make it challenging to track moving objects or scan the environment effectively.
Difficulty focusing on objects located laterally is another symptom of abducens nerve palsy. The affected eye may have difficulty fixating on objects that are positioned towards the side opposite to the affected nerve. This can cause visual discomfort and impact daily activities that require accurate depth perception and peripheral vision.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate treatment options.
Treatment Options for Abducens Nerve Disorders
Treatment for abducens nerve disorders will depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. It is essential to consult with a qualified ophthalmologist or neurologist who can accurately diagnose the problem and prescribe the most suitable treatment approach.
Visual aids, such as prism glasses or eye patches, may be recommended to alleviate double vision and improve visual alignment. These aids help redirect the light entering the eyes, allowing for better fusion of the images and reducing the perception of double vision.
Eye exercises, also known as orthoptic exercises, can be beneficial in strengthening the eye muscles and improving eye coordination. These exercises involve controlled eye movements and may be performed under the guidance of a trained eye care professional. They can help improve eye alignment and reduce the severity of symptoms in some cases.
In certain situations, medications may be prescribed to manage underlying conditions contributing to abducens nerve disorders. For example, anti-inflammatory drugs may be used to reduce inflammation around the nerve, while antibiotics can help treat infections that may be causing the dysfunction.
In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail to provide adequate improvement, surgery may be considered. Surgical interventions aim to correct the underlying cause of the nerve dysfunction or address any structural abnormalities that may be affecting the nerve’s function.
However, it is important to remember that each case is unique, and treatment recommendations should be based on individual consultation with a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for maximizing the chances of successful treatment and minimizing long-term visual complications.
Recent Research on the Abducens Nerve and Eye Muscles
Advancements in scientific research have provided valuable insights into our understanding of the abducens nerve and its relationship with the extrinsic eye muscles. Let’s explore some recent research findings and future directions in eye muscle research.
Advances in Understanding the Abducens Nerve
Ongoing research has shed new light on the intricate functioning of the abducens nerve and its role in eye movement control. Researchers continue to investigate the molecular mechanisms and neural circuitry underlying the precise coordination of eye muscles.
One recent study conducted at a renowned neuroscience institute focused on mapping the neural connections of the abducens nerve. By using advanced imaging techniques, the researchers were able to identify the specific pathways through which the nerve sends signals to the lateral rectus muscle, responsible for the outward movement of the eye. This groundbreaking discovery has opened up new avenues for understanding the complex interplay between the abducens nerve and the eye muscles.
Another research project explored the role of the abducens nerve in different eye movement disorders. By studying patients with conditions such as strabismus and nystagmus, the researchers were able to pinpoint specific abnormalities in the functioning of the abducens nerve. These findings have paved the way for targeted therapeutic interventions aimed at correcting these disorders and improving patients’ quality of life.
Future Directions in Eye Muscle Research
The exploration of eye muscle function and the intricate connections between cranial nerves is an area of active research. Scientists and healthcare professionals are continually striving to improve our understanding of eye muscle disorders and develop more targeted and effective treatments.
One promising avenue of future research is the development of innovative therapies for individuals with abducens nerve palsy. Researchers are currently investigating the potential of gene therapy to restore the function of the abducens nerve and improve eye movement control. Preliminary studies in animal models have shown promising results, raising hopes for a breakthrough in the treatment of this debilitating condition.
Additionally, advancements in neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), are enabling researchers to study the real-time activity of the abducens nerve and its connections with other brain regions involved in eye movement control. This cutting-edge technology holds great potential for unraveling the complex neural networks underlying eye muscle function and providing insights into the mechanisms of eye movement disorders.
In conclusion, the abducens nerve innervates the lateral rectus muscle, allowing for the lateral movement of the eye. By working in coordination with the extrinsic eye muscles, the abducens nerve ensures that our eye movements are precise and synchronized. However, it is important to recognize that disorders related to the abducens nerve can impact eye movements and visual function. It is advisable to seek professional medical advice and consultation if you experience any concerning symptoms related to the abducens nerve or extrinsic eye muscles. By staying informed and proactive, we can better understand and address any potential issues affecting our visual health.
Leave a Reply