The abducens nerve, also known as cranial nerve VI, plays a significant role in our ability to control eye movements. This nerve is responsible for innervating the lateral rectus muscle, which allows the eye to move laterally or towards the side of the head. Understanding the functionality and importance of the abducens nerve is crucial to comprehending its impact on our daily lives.
Understanding the Abducens Nerve
The abducens nerve is a crucial component of the nervous system, responsible for facilitating controlled and coordinated eye movements. Its anatomy and role in the nervous system are fascinating and worth exploring in detail.
Anatomy of the Abducens Nerve
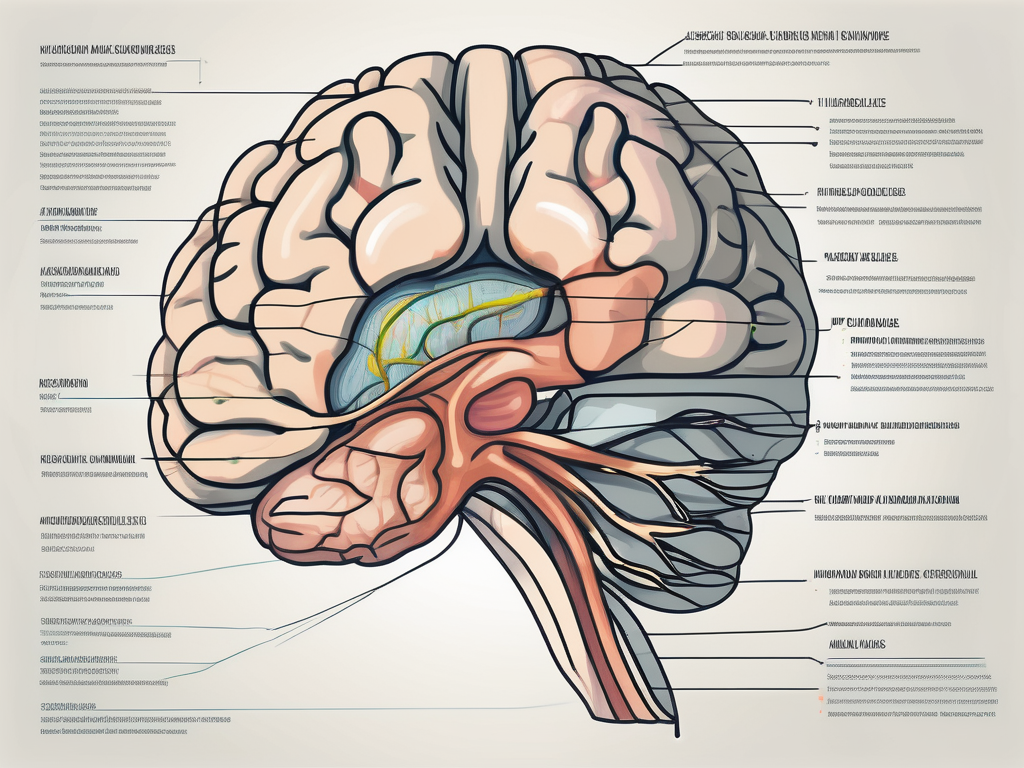
The abducens nerve originates from the abducens nucleus, a group of motor neurons located within the pons region of the brainstem. This nucleus serves as the command center for the nerve, sending signals that initiate eye movements. From its origin, the abducens nerve embarks on a complex journey.
After leaving the abducens nucleus, the nerve enters the cavernous sinus, a cavity located within the skull. This sinus serves as a protective pathway for the nerve, shielding it from potential damage. As the abducens nerve courses through the cavernous sinus, it navigates through a maze of blood vessels and other structures, ensuring its safe passage.
Eventually, the abducens nerve reaches its destination: the superior orbital fissure. This narrow opening in the skull allows the nerve to access the orbit, the bony socket that houses the eye. Upon entering the orbit, the abducens nerve finally connects with its target: the lateral rectus muscle.
The lateral rectus muscle is one of the six extraocular muscles responsible for controlling eye movements. When the abducens nerve sends signals to the lateral rectus muscle, it contracts, causing the eye to move laterally away from the midline. This movement is known as abduction, hence the name of the nerve.
The intricate pathway of the abducens nerve highlights its vulnerability to various disorders. Any disruption along its course, whether due to trauma, inflammation, or compression, can lead to impaired eye movements and vision problems.
The Role of the Abducens Nerve in the Nervous System
As part of the cranial nerve system, the abducens nerve plays a vital role in facilitating coordinated eye movements. It works in harmony with other cranial nerves to ensure accurate visual tracking and proper alignment of our gaze.
One of its primary collaborators is the oculomotor nerve, which controls the majority of the eye’s movements. The abducens nerve and the oculomotor nerve work together to execute horizontal eye movements. When the abducens nerve signals the lateral rectus muscle to contract, the oculomotor nerve simultaneously signals the medial rectus muscle to relax, allowing the eye to move smoothly and accurately.
Another cranial nerve that interacts with the abducens nerve is the trochlear nerve. The trochlear nerve controls the superior oblique muscle, which is responsible for downward and inward eye movements. The abducens nerve and the trochlear nerve work together to ensure precise and coordinated vertical eye movements.
Additionally, the abducens nerve collaborates with the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve, which provides sensory innervation to the eye and surrounding structures. This collaboration allows for the integration of sensory feedback with motor commands, ensuring optimal eye movements and visual perception.
Overall, the abducens nerve’s role in the nervous system is crucial for maintaining proper eye function. Its intricate connections and coordination with other cranial nerves enable us to navigate the world visually with accuracy and precision.
Functions of the Abducens Nerve
The abducens nerve, also known as cranial nerve VI, plays a vital role in controlling various aspects of eye movement and facial expressions. Let’s delve deeper into its functions and understand its significance in our daily lives.
Control of Eye Movement
The primary function of the abducens nerve is to control lateral eye movements, specifically abduction of the eye. This movement allows the eye to rotate outwardly, enabling us to look towards the side. It works in conjunction with other cranial nerves, such as the oculomotor and trochlear nerves, to ensure smooth and coordinated eye movements.
Imagine walking down a bustling street, trying to cross the road. Your abducens nerve is actively engaged, allowing your eyes to scan the surroundings, ensuring you can spot any oncoming vehicles from the sides. This ability to move our eyes laterally is crucial for our safety and well-being.
Additionally, the abducens nerve assists in maintaining binocular vision, a crucial aspect of depth perception. Binocular vision allows us to perceive the world in three dimensions, accurately judging distances and spatial relationships. This ability is essential for tasks such as catching a ball, driving, or even pouring a glass of water without spilling.
Role in Facial Expressions
Although the primary focus of the abducens nerve is eye movement, it also contributes to facial expressions. The abducens nerve connects with the facial nerve, enabling coordinated actions such as blinking, squinting, and narrowing of the eyes.
Think about how your face reacts when you see something surprising or funny. Your abducens nerve is responsible for the rapid blinking that occurs when you burst into laughter or the narrowing of your eyes when you squint to get a better look at something. These subtle movements add depth and emotion to our facial expressions, allowing us to communicate non-verbally with others.
This interaction between the abducens nerve and the facial nerve showcases the intricate interplay between various cranial nerves and their collective influence on our facial expressions. It highlights the complexity of our nervous system and how different parts work together seamlessly to create the rich tapestry of human expression.
In conclusion, the abducens nerve is a crucial component of our visual and facial systems. Its ability to control lateral eye movements and contribute to facial expressions enhances our daily experiences, allowing us to navigate the world with precision and express our emotions effectively.
Disorders Related to the Abducens Nerve
The abducens nerve plays a crucial role in eye movement, specifically in controlling the lateral rectus muscle. When this nerve is affected, it can lead to a condition known as abducens nerve palsy. This condition is characterized by weakness or paralysis of the lateral rectus muscle, which can result in various symptoms and complications.
Causes of Abducens Nerve Palsy
Abducens nerve palsy can occur due to a range of factors. One common cause is trauma, such as head injuries or fractures that affect the cranial nerves. Vascular disorders, including aneurysms or ischemic strokes, can also lead to abducens nerve palsy by disrupting the blood supply to the nerve. In some cases, tumors, both benign and malignant, can exert pressure on the nerve, causing dysfunction. Furthermore, infections, such as meningitis or sinusitis, can affect the abducens nerve and result in palsy. It is important to note that underlying medical conditions like diabetes or multiple sclerosis can also contribute to the development of abducens nerve disorders.
If you experience sudden or persistent changes in your eye movement, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage the symptoms and prevent further complications.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Abducens Nerve Disorders
The symptoms associated with abducens nerve disorders can vary depending on the extent of nerve damage. One common symptom is a noticeable inward deviation of the affected eye, leading to double vision or diplopia. This occurs because the lateral rectus muscle is unable to properly move the eye outward, resulting in misalignment. Individuals with abducens nerve palsy may also experience difficulty moving the affected eye in a horizontal direction, leading to limited eye mobility.
In addition to visual disturbances, abducens nerve disorders can cause eye strain and headaches. The extra effort required to compensate for the impaired eye movement can strain the eye muscles and lead to discomfort. Headaches may also occur due to the strain placed on the visual system.
Diagnosing abducens nerve disorders typically involves a comprehensive examination by a healthcare professional. This examination includes a detailed medical history to identify any underlying conditions or potential causes. A physical assessment will be conducted to evaluate eye movements, muscle strength, and coordination. In some cases, additional tests may be necessary, such as imaging tests like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans to assess the structures surrounding the abducens nerve. Specialized eye exams, such as ocular motility testing or electroretinography, may also be performed to further evaluate the function of the abducens nerve.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in managing abducens nerve disorders. Treatment options may include addressing the underlying cause, such as treating infections or managing underlying medical conditions. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve pressure on the nerve or correct any structural abnormalities. Additionally, vision therapy or eye exercises may be recommended to improve eye coordination and strengthen the affected eye muscles.
Treatment and Management of Abducens Nerve Disorders
The treatment options for abducens nerve disorders depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. While some cases may require medical intervention, such as the management of underlying medical conditions or surgical approaches to address specific abnormalities or injuries, others may benefit from non-invasive techniques like prism glasses. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and advice.
When it comes to medical interventions for abducens nerve palsy, there are various approaches that can be considered. One common method is the management of underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the disorder. For example, if the abducens nerve palsy is caused by diabetes, controlling blood sugar levels through medication and lifestyle changes may help improve the condition.
In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. This could involve addressing specific abnormalities or injuries that are affecting the abducens nerve. For instance, if there is a tumor pressing on the nerve, surgical removal of the tumor may be required to alleviate the symptoms.
However, not all cases of abducens nerve disorders require invasive procedures. Non-invasive techniques like prism glasses can be used to manage the condition. Prism glasses work by altering the way light enters the eye, thus helping to correct the alignment of the eyes and improve double vision. These glasses can be prescribed by an eye care professional and are often a convenient and effective option for those with mild to moderate abducens nerve disorders.
Rehabilitation and Therapy Options
In certain cases of abducens nerve disorders, rehabilitation and therapy can play a crucial role in optimizing visual function. Vision therapy, ocular exercises, or specialized rehabilitative techniques may be recommended to enhance eye coordination, strengthen eye muscles, and improve overall visual performance. These approaches are often tailored to individual needs and should be conducted under the guidance of a qualified eye care professional.
Vision therapy involves a series of exercises and activities designed to improve eye movement, focusing abilities, and visual processing skills. These exercises can help train the eyes to work together more effectively, reducing symptoms such as double vision and eye strain. Ocular exercises, on the other hand, target specific eye muscles to improve their strength and flexibility.
In addition to vision therapy and ocular exercises, specialized rehabilitative techniques may also be employed. These techniques can include the use of prisms, filters, or other visual aids to help compensate for any visual deficits caused by the abducens nerve disorder. The goal of rehabilitation and therapy is to improve visual function and quality of life for individuals with abducens nerve disorders.
It is important to note that rehabilitation and therapy options should be tailored to each individual’s specific needs and condition. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with an eye care professional who specializes in vision therapy and rehabilitation to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
The Impact of Abducens Nerve Disorders on Daily Life
Challenges in Visual Perception
Abducens nerve disorders can significantly affect one’s visual perception and quality of life. Difficulties in maintaining eye alignment or coordinating eye movements can lead to blurred or double vision, impaired depth perception, and challenges in tasks requiring accurate visual tracking, such as reading, driving, or participating in sports. These challenges can be frustrating and may impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities with ease and confidence.
Imagine trying to read a book, but the words appear blurry and distorted. The effort required to decipher the text can be mentally and physically exhausting. Even simple tasks like crossing the street or catching a ball become daunting when your eyes struggle to work together. The constant strain on the eyes can lead to headaches, eye fatigue, and decreased productivity.
However, it is essential to remember that with appropriate diagnosis, management, and potential rehabilitative measures, these challenges can often be mitigated. Vision therapy, for example, is a non-invasive treatment option that focuses on improving eye alignment, coordination, and visual processing skills. Through a series of exercises and activities, individuals can regain control over their eye movements and enhance their overall visual function.
Coping Strategies and Support Systems
For individuals dealing with the impact of abducens nerve disorders, it is crucial to explore coping strategies and establish a support system. This may involve seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, connecting with support groups or communities, and implementing lifestyle modifications to optimize visual function.
Support groups can provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, exchange tips and advice, and find solace in knowing that they are not alone in their journey. These communities foster a sense of understanding, empathy, and encouragement, which can be invaluable when navigating the challenges of living with an abducens nerve disorder.
Implementing lifestyle modifications can also make a significant difference in managing the impact of these disorders. Simple adjustments, such as using larger fonts or magnifying tools for reading, organizing workspaces to minimize visual distractions, and taking regular breaks to rest the eyes, can help reduce strain and improve overall visual comfort.
While each individual’s experience is unique, fostering a positive mindset and embracing available resources can significantly contribute to one’s overall well-being and adaptability in daily life. It is important to remember that living with an abducens nerve disorder does not define a person’s capabilities or limit their potential for growth and success.
With the right support and a proactive approach, individuals can develop resilience, learn effective coping strategies, and find ways to thrive despite the challenges they face. It is a journey that requires patience, determination, and a willingness to explore different options, but the rewards of improved visual function and a higher quality of life are well worth the effort.
In conclusion, the abducens nerve, through its intricate anatomy and functions, plays a pivotal role in the control of eye movement and facial expressions. Disorders related to the abducens nerve can present unique challenges but can often be managed through various treatment options and therapeutic approaches. If you have concerns about your eye movement or are experiencing any symptoms related to abducens nerve disorders, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized guidance. The journey towards optimum visual health begins with understanding and proactive care.
Leave a Reply