The abducens nerve, also known as cranial nerve VI, is responsible for controlling the lateral rectus muscle. Understanding the complex relationship between these two structures is essential to comprehending their role in eye movement and the potential impact of abducens nerve disorders.
Understanding the Abducens Nerve
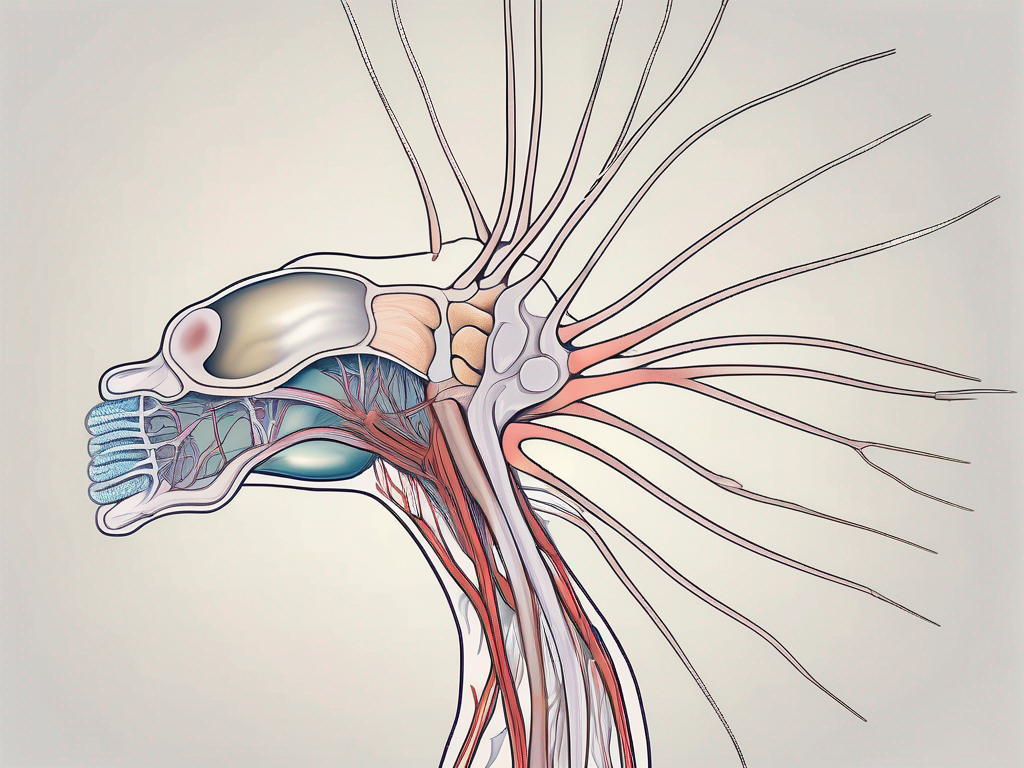
Before delving into the specific muscle it controls, let’s take a moment to understand the anatomy and function of the abducens nerve itself. This cranial nerve originates from the pons, a region in the brainstem. As one of the twelve cranial nerves, its primary function is to control specific muscles in the head and neck.
The abducens nerve, also known as cranial nerve VI, is a vital component of the nervous system. It plays a crucial role in coordinating eye movements and ensuring our vision remains aligned and accurate. Without the abducens nerve, our eyes would struggle to move in unison, leading to difficulties in tracking objects and maintaining visual focus.
Anatomy of the Abducens Nerve
The abducens nerve follows a trajectory from its origin in the brainstem to the eye socket, where it innervates the lateral rectus muscle. This muscle is responsible for the horizontal movement of the eye, allowing us to gaze away from the midline. The intricate pathway of the abducens nerve involves traversing through various critical structures, ensuring its proper functioning.
One of the notable structures the abducens nerve passes through is the cavernous sinus. This venous structure, located on each side of the skull, houses several important nerves and blood vessels. The abducens nerve’s journey through the cavernous sinus exposes it to potential compression or damage, which can lead to a condition known as abducens nerve palsy. This condition manifests as an inability to move the affected eye laterally, resulting in double vision and difficulties in focusing.
Continuing its course, the abducens nerve traverses the superior orbital fissure, a narrow opening in the skull located behind the eye socket. This passage allows the nerve to reach its destination, the lateral rectus muscle, which it innervates. The intricate nature of this pathway highlights the vulnerability of the abducens nerve to various pathological processes, such as tumors, inflammation, or trauma, which can disrupt its normal function.
Function of the Abducens Nerve
The main function of the abducens nerve is to facilitate horizontal movement of the eye by contracting the lateral rectus muscle. This muscle acts as a pulley, pulling the eye laterally, thus allowing us to gaze away from the midline. The coordinated action of both abducens nerves ensures that our eyes move in harmony, enabling us to explore our surroundings and engage in activities that require visual tracking.
When the abducens nerve is functioning optimally, it allows us to smoothly shift our gaze from one point to another, effortlessly following moving objects. This ability is particularly crucial in activities such as reading, driving, and playing sports, where accurate eye movements are essential for optimal performance.
However, when the abducens nerve is compromised, whether due to injury, disease, or other factors, it can result in a condition called abducens nerve palsy. This condition leads to a limited or complete loss of lateral eye movement on the affected side. Individuals with abducens nerve palsy may experience difficulties in focusing, double vision, and a reduced ability to track moving objects.
In conclusion, the abducens nerve is a vital component of the nervous system, responsible for coordinating horizontal eye movements. Its intricate anatomy and function highlight its importance in maintaining visual alignment and accurate gaze. Understanding the abducens nerve’s role in eye movement can provide valuable insights into various conditions that can affect its function, ultimately leading to a better understanding of the complexities of the human visual system.
The Muscle Controlled by the Abducens Nerve
Now that we have a solid understanding of the abducens nerve, let’s delve deeper into the fascinating muscle it controls – the lateral rectus muscle. This muscle, although often overlooked, plays a crucial role in eye movement and coordination, ensuring that our visual field covers a wide range of directions.
The lateral rectus muscle is one of the six extraocular muscles responsible for controlling the movement of the eye. It is located on the outer side of the eye socket and receives innervation from the abducens nerve. This muscle’s primary function is to abduct the eye, meaning it moves the eye away from the midline.
When the abducens nerve stimulates the lateral rectus muscle, an intricate process of coordinated eye movement takes place. This muscle’s contraction allows our eyes to gaze towards the side, providing binocular vision and facilitating an expansive visual field.
In combination with the other extraocular muscles, the lateral rectus muscle maintains precise control over eye movements. The partnership between the abducens nerve and the lateral rectus muscle assures the fluidity and accuracy of horizontal eye movement.
But what happens if there is a dysfunction in the abducens nerve or the lateral rectus muscle? Well, it can lead to a condition called abducens nerve palsy. This condition can result in the inability to move the affected eye laterally, causing double vision and difficulty in focusing on objects to the side.
Interestingly, the lateral rectus muscle not only plays a role in eye movement but also contributes to facial expressions. When we squint or narrow our eyes, the lateral rectus muscle is involved in this action. It helps us convey emotions such as skepticism, concentration, or even playfulness.
Furthermore, the lateral rectus muscle is not only important for humans but also for animals. For instance, predatory animals like lions and tigers heavily rely on their lateral rectus muscles to accurately track and pursue their prey. This muscle enables them to maintain visual contact with their target, ensuring a successful hunt.
It’s also worth noting that the lateral rectus muscle can be affected by certain medical conditions. For instance, in individuals with Duane syndrome, a rare congenital disorder, the lateral rectus muscle may be partially or completely paralyzed. This leads to restricted eye movement, making it challenging to look towards the affected side.
In conclusion, the lateral rectus muscle, controlled by the abducens nerve, is a remarkable component of our visual system. Its ability to abduct the eye, facilitate binocular vision, and contribute to facial expressions showcases its importance in our daily lives. Understanding the intricate relationship between the abducens nerve and the lateral rectus muscle allows us to appreciate the complexity and beauty of our visual system.
The Relationship between the Abducens Nerve and Lateral Rectus Muscle
The abducens nerve and the lateral rectus muscle work in perfect harmony to facilitate lateral eye movement. This intricate connection between the brain and the muscle allows for precise and coordinated eye motions in the desired direction.
When the brain sends a command to move the eye laterally, the abducens nerve comes into action. This vital nerve acts as a messenger, carrying the signal from the brainstem to the lateral rectus muscle. The abducens nerve stimulates the lateral rectus muscle, prompting it to contract and initiate the desired eye movement.
Imagine a scenario where you want to shift your gaze to the side. The abducens nerve receives the command from your brain and transmits it to the lateral rectus muscle. This muscle, located on the outer side of the eye, contracts in response to the signal, causing the eye to move laterally. This coordinated effort ensures smooth and precise eye movement in the intended direction.
How the Abducens Nerve Stimulates the Lateral Rectus Muscle
The abducens nerve plays a crucial role in the stimulation of the lateral rectus muscle. This nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, originates in the brainstem and travels through the skull to reach the lateral rectus muscle.
Upon receiving the command to move the eye laterally, the abducens nerve releases neurotransmitters that bind to receptors on the surface of the lateral rectus muscle fibers. This binding process triggers a cascade of events within the muscle, leading to its contraction. As the lateral rectus muscle contracts, it exerts a pulling force on the eye, causing it to move laterally.
It is fascinating to think about the intricate communication between the abducens nerve and the lateral rectus muscle. This seamless interaction allows us to effortlessly shift our gaze from one point to another, enhancing our visual perception and overall experience of the world.
Impact of Abducens Nerve Damage on the Lateral Rectus Muscle
While the relationship between the abducens nerve and the lateral rectus muscle is usually harmonious, disruptions to their normal functioning can have significant consequences.
Conditions such as abducens nerve palsy, nerve compression, or trauma can result in limited or absent eye abduction. Abducens nerve palsy refers to the paralysis or weakness of the abducens nerve, leading to an inability to move the eye laterally. This condition can be caused by various factors, including infections, tumors, or vascular disorders.
When the abducens nerve is damaged or compromised, the communication between the brain and the lateral rectus muscle is disrupted. As a result, the lateral rectus muscle may not receive the necessary stimulation to contract, leading to difficulties in moving the eye laterally.
Patients experiencing symptoms such as double vision, eye misalignment, or difficulty moving the eye laterally should seek medical attention promptly. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional can help determine the underlying cause of the abducens nerve dysfunction and guide appropriate management strategies.
Understanding the impact of abducens nerve damage on the lateral rectus muscle highlights the intricate nature of our visual system. It serves as a reminder of the delicate balance required for optimal eye movement and the importance of seeking timely medical intervention when abnormalities arise.
Disorders Related to the Abducens Nerve
The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in eye movement. When this nerve is affected by certain disorders, it can lead to a condition known as abducens nerve palsy. This condition is characterized by the dysfunction of the abducens nerve, which can have several causes.
Causes of Abducens Nerve Palsy
Abducens nerve palsy can be caused by a variety of factors. One common cause is head trauma, which can result in damage to the nerve and disrupt its normal functioning. Infections, such as meningitis or sinusitis, can also affect the abducens nerve and lead to palsy.
Individuals with diabetes may be at a higher risk of developing abducens nerve disorders. The elevated blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can cause damage to the nerves, including the abducens nerve. Additionally, certain medications, such as those used to treat high blood pressure or seizures, have been linked to abducens nerve palsy as a potential side effect.
It is important to note that each case of abducens nerve palsy requires individual evaluation to pinpoint the exact underlying factor contributing to the condition. A comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests may be necessary to determine the cause and guide appropriate treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Abducens Nerve Disorders
Abducens nerve disorders can manifest in various symptoms, which can significantly impact an individual’s vision and eye movement. One common symptom is double vision, also known as diplopia. This occurs when the eyes are unable to align properly, causing images to appear duplicated.
Another symptom of abducens nerve disorders is difficulty moving the eye laterally. The abducens nerve is responsible for the lateral movement of the eye, allowing it to move towards the outer side of the face. When the nerve is affected, individuals may experience limitations in their ability to move their eyes in this direction.
Improper alignment of the eyes, known as strabismus, is another common symptom associated with abducens nerve disorders. This misalignment can lead to a condition called esotropia, where one eye turns inward while the other remains straight.
If an individual experiences any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek professional guidance for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. An ophthalmologist or neurologist will conduct a thorough examination, which may involve visual acuity tests, eye movement evaluations, and imaging studies. These diagnostic measures help determine the extent of the nerve damage and guide the development of a personalized treatment plan.
In conclusion, disorders related to the abducens nerve can have various causes, including head trauma, infections, diabetes, tumors, and certain medications. The symptoms of these disorders can significantly impact an individual’s vision and eye movement. Seeking professional medical evaluation is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of abducens nerve disorders.
Treatment and Recovery for Abducens Nerve Damage
Medical Interventions for Abducens Nerve Disorders
The treatment approach for abducens nerve damage depends on the underlying cause and severity. In some cases, conservative management, such as patching or prism glasses, may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms. Patching involves covering one eye to reduce double vision and allow the affected eye to rest and recover. Prism glasses, on the other hand, use specially designed lenses to help align the eyes and reduce strain on the abducens nerve.
However, more severe cases of abducens nerve damage may require more invasive interventions. Surgical procedures, such as strabismus surgery, can be performed to correct misalignment of the eyes. During this procedure, the surgeon adjusts the tension of the eye muscles to improve eye alignment and restore normal movement. Another surgical option is decompression surgery, which involves relieving pressure on the abducens nerve to restore its function.
In addition to surgical interventions, targeted medical therapies may also be used to treat abducens nerve disorders. Medications, such as corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory drugs, or immunosuppressants, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and promote nerve healing. These medications can help alleviate symptoms and improve the overall prognosis for individuals with abducens nerve damage.
Prognosis and Rehabilitation for Abducens Nerve Damage
Recovery from abducens nerve damage varies from person to person and heavily depends on the cause and extent of the injury. With proper medical guidance and appropriate rehabilitative measures, many individuals can regain satisfactory eye movement.
Rehabilitation for abducens nerve damage often involves a combination of exercises and therapies aimed at improving eye coordination and strengthening the eye muscles. Eye exercises, such as tracking objects or focusing on different distances, can help improve eye movement and reduce double vision. Vision therapy, conducted by trained professionals, may also be recommended to address specific visual impairments associated with abducens nerve damage.
Furthermore, lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in the recovery process. Resting the eyes regularly, maintaining proper hydration, and adopting a balanced diet rich in nutrients essential for nerve health, such as vitamins B12 and E, can support the healing process and optimize recovery.
However, it is essential to remain realistic and understand that full recovery may not always be possible. Some individuals may experience residual symptoms or limitations in eye movement even after treatment and rehabilitation. Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals is crucial to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
In conclusion, the lateral rectus muscle is controlled by the abducens nerve, ensuring the accurate movement of our eyes towards the side. Understanding the anatomy, function, and interplay between these two structures is essential to grasp the potential impact of abducens nerve disorders. If you believe you are experiencing any abnormalities related to eye movement, consult with a healthcare professional to receive appropriate evaluation and guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Leave a Reply