The human eye is a complex organ that allows us to perceive the world around us. To understand the connection between the abducens nerve (CN VI) and eye movement, it is essential to have a basic understanding of the anatomy of the eye.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Eye
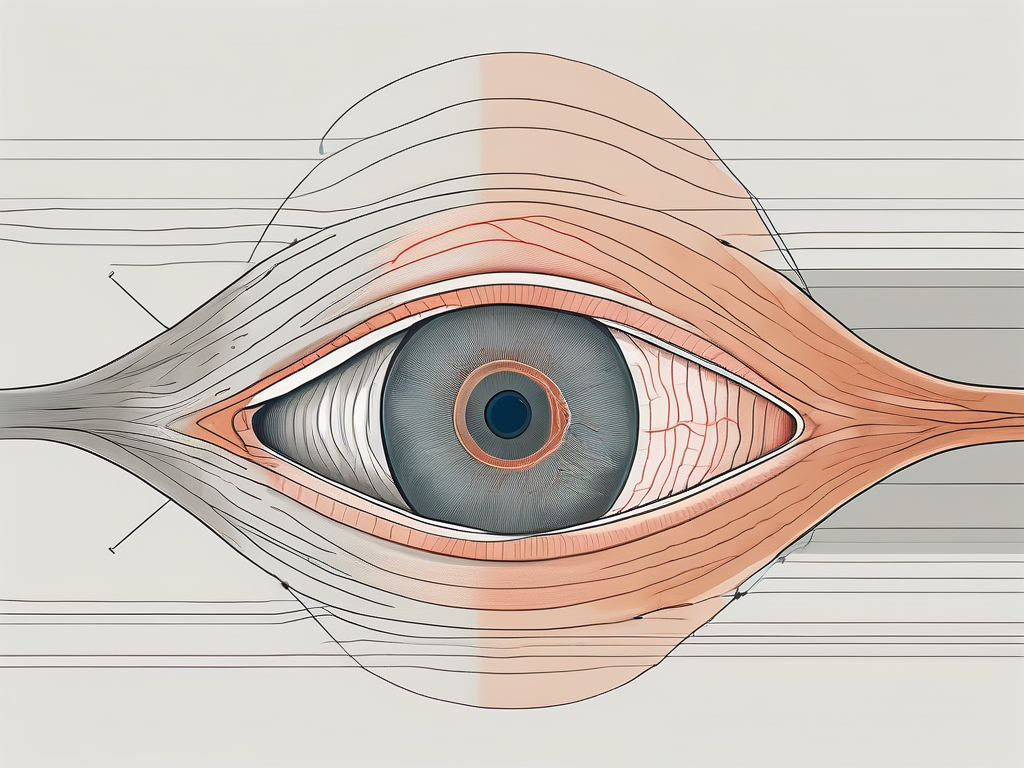
The eye is a fascinating sensory organ that enables us to see the world around us. It consists of several intricate structures, each with its own unique function, working together to create the miracle of vision.
One of the key structures of the eye is the cornea, a transparent dome-shaped layer that covers the front part of the eye. The cornea acts as a protective shield, allowing light to enter the eye and focusing it onto the lens.
Speaking of the lens, it is a flexible, transparent structure located behind the iris. The lens plays a crucial role in focusing light onto the retina, which is a layer of light-sensitive cells located at the back of the eye. These cells convert light into electrical signals that are then transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve.
The pupil, a small opening in the center of the iris, regulates the amount of light entering the eye. In bright light, the pupil constricts to reduce the amount of light, while in dim light, it dilates to allow more light to enter.
Now, let’s delve into the fascinating world of eye movement. The extrinsic eye muscles, a group of six muscles, are responsible for controlling the movement of the eye. These muscles work together in perfect harmony, allowing us to track objects, focus our gaze, and perform intricate eye movements.
The Role of Extrinsic Eye Muscles
The extrinsic eye muscles include the medial rectus, lateral rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, superior oblique, and inferior oblique. Each of these muscles has a specific function in controlling eye movement.
The medial rectus muscle, for example, is responsible for moving the eye inward, towards the nose. On the other hand, the lateral rectus muscle moves the eye outward, away from the nose. The superior rectus muscle elevates the eye, while the inferior rectus muscle depresses it. The superior oblique muscle helps to rotate the eye downward and away from the nose, while the inferior oblique muscle rotates the eye upward and away from the nose.
These muscles work in perfect coordination, allowing us to explore our surroundings, follow moving objects, and shift our gaze from one point to another with remarkable precision.
The Importance of the Abducens Nerve (CN VI)
Now, let’s talk about the abducens nerve, also known as cranial nerve VI. This nerve plays a critical role in the control of eye movement, specifically in the lateral movement of the eye.
The abducens nerve originates in the brainstem and innervates the lateral rectus muscle. This muscle is responsible for turning the eye outward, away from the nose. Without the abducens nerve, our eyes would not be able to work together in harmony, leading to difficulties in coordinating eye movements.
Thanks to the abducens nerve, our eyes can smoothly and effortlessly move laterally, allowing us to explore our surroundings, scan our environment, and maintain a clear and focused vision.
In conclusion, the eye is a complex and remarkable organ that enables us to perceive the world around us. From the transparent cornea to the intricate extrinsic eye muscles and the vital abducens nerve, each component plays a crucial role in the intricate dance of vision. Understanding the anatomy of the eye not only deepens our appreciation for this incredible organ but also helps us comprehend the wonders of sight.
The Connection between the Abducens Nerve and Eye Muscles
Eye movement is a complex process that requires precise coordination between the nerves and muscles. The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in this intricate dance. It communicates signals from the brain to the lateral rectus muscle, instructing it to move the eye outward. This coordinated action allows for horizontal eye movement, enabling us to scan our surroundings and focus on objects of interest.
But how exactly does the abducens nerve control eye movement? Let’s delve deeper into the fascinating mechanics behind this process.
How the Abducens Nerve Controls Eye Movement
When we desire to look towards one side, the abducens nerve springs into action. It sends electrical signals, known as action potentials, to the lateral rectus muscle on the opposite side, causing it to contract. This contraction pulls the eye away from the midline, allowing us to direct our gaze outward.
Imagine you’re walking down a bustling street, and suddenly, something catches your eye on the left side. Your brain swiftly sends signals through the abducens nerve, commanding the right lateral rectus muscle to contract. As a result, your right eye turns outward, focusing on the intriguing sight. This seamless coordination between the abducens nerve and the lateral rectus muscle allows for smooth eye movement and effortless exploration of our environment.
The Specific Eye Muscle Innervated by the Abducens Nerve
While the abducens nerve is responsible for controlling eye movement, it exclusively innervates the lateral rectus muscle of the eye. This unique innervation ensures precise control over the outward movement of the eye, contributing to our ability to explore our environment and engage with the world around us.
The lateral rectus muscle, located on the outer side of each eye, acts as a powerful partner to the abducens nerve. When the abducens nerve sends signals to this muscle, it responds with remarkable precision, allowing us to shift our gaze horizontally. This intricate connection between the abducens nerve and the lateral rectus muscle is a testament to the intricate design of our visual system.
Next time you find yourself effortlessly scanning your surroundings or fixating on an object of interest, take a moment to appreciate the intricate dance between the abducens nerve and the lateral rectus muscle. Their partnership enables us to navigate the world with ease, constantly expanding our horizons and soaking in the wonders around us.
Potential Health Implications of Abducens Nerve Dysfunction
When there is dysfunction or damage to the abducens nerve, it can result in a condition known as abducens nerve palsy. This condition affects the ability to move the affected eye laterally, leading to various vision disturbances.
The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, is responsible for the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, which allows the eye to move outward. When this nerve is not functioning properly, it can cause a range of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s visual functioning and overall quality of life.
One of the most common symptoms of abducens nerve palsy is double vision, also known as diplopia. This occurs when the eyes are not properly aligned, causing the brain to receive two different images. This can make it difficult to focus on objects, read, or perform tasks that require precise visual coordination.
In addition to double vision, individuals with abducens nerve palsy may also experience difficulty moving the affected eye outward. This can make it challenging to track moving objects or to shift focus from one point to another. It can also affect depth perception, making it harder to judge distances accurately.
Misalignment of the eyes, known as strabismus, is another common symptom of abducens nerve palsy. This occurs when one eye deviates from its normal position, causing the eyes to appear crossed or misaligned. Strabismus can not only affect a person’s appearance but can also lead to further vision problems if left untreated.
Symptoms of Abducens Nerve Palsy
Some common symptoms of abducens nerve palsy include double vision, difficulty moving the affected eye outward, and misalignment of the eyes. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s visual functioning, making everyday tasks challenging.
Individuals with abducens nerve palsy may find it difficult to drive, as their ability to accurately judge distances and track moving objects is compromised. Simple tasks such as reading, writing, or using a computer can also become more challenging due to the double vision and difficulty in focusing on a single point.
Furthermore, the misalignment of the eyes can lead to self-consciousness and social anxiety, as individuals may feel uncomfortable making eye contact or worry about how others perceive their appearance. This can have a significant impact on a person’s self-esteem and overall well-being.
Treatment Options for Abducens Nerve Disorders
If you suspect you have abducens nerve palsy or any eye-related concerns, it is essential to consult with an experienced ophthalmologist or healthcare professional. They will conduct a thorough examination and may perform additional tests to determine the underlying cause of the dysfunction.
Treatment options for abducens nerve disorders may include eye exercises, prism glasses, medications, or in severe cases, surgical interventions. Eye exercises can help strengthen the eye muscles and improve coordination, while prism glasses can help correct the alignment of the eyes and reduce double vision.
Medications such as botulinum toxin injections may be used to temporarily weaken specific eye muscles, allowing the unaffected muscles to compensate for the dysfunction. In severe cases where conservative measures are ineffective, surgical interventions may be considered to correct the underlying issue and restore normal eye movement.
Proper diagnosis and care are crucial to improving visual function and quality of life for individuals with abducens nerve disorders. It is important to follow the recommended treatment plan and attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment approach.
Living with abducens nerve dysfunction can be challenging, but with the right medical care and support, individuals can manage their symptoms and regain a good quality of life. It is important to seek help early and not delay treatment, as early intervention can often lead to better outcomes.
The Science Behind Eye Movement and Vision
Eye movement and vision are incredibly intricate processes that involve the complex interplay of nerves, muscles, and cognitive processing. Understanding the science behind these processes can provide valuable insights into how our eyes work and how we perceive the world.
When we think about eye movement, we often focus on the muscles and nerves involved. However, it is essential to recognize that eye movement is not just a mechanical process. It is also influenced by our cognitive abilities and the way our brain processes visual information.
The Role of Nerves in Eye Function
The nerves in the eyes play a vital role in transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain. These signals allow us to interpret the visual world and make sense of the images we see. One of the key nerves involved in eye movement is the abducens nerve (CN VI).
The abducens nerve is responsible for innervating the lateral rectus muscle, which allows for outward eye movement. This muscle is crucial for horizontal eye movements, such as when we look from side to side. Dysfunction of the abducens nerve can lead to a condition known as abducens nerve palsy, which affects eye coordination and visual function.
However, the abducens nerve is just one part of this intricate network of nerve pathways that work together to ensure optimal visual functioning. Other nerves, such as the oculomotor nerve (CN III) and the trochlear nerve (CN IV), play important roles in controlling different eye movements, including vertical and rotational movements.
The Complex Interplay of Muscles and Nerves in Vision
Vision is not merely a result of the eyes capturing light; it is a complex interplay between the extrinsic eye muscles, cranial nerves, and the brain. The coordination of these structures allows for precise eye movements, focus adjustments, and the ability to recognize and interpret visual stimuli.
For example, when we read a book, our eyes move in a series of rapid, precise movements called saccades. These movements allow us to scan the text and focus on different words and sentences. The muscles and nerves involved in these eye movements work together seamlessly, guided by the information processed by our brain.
Furthermore, our eyes have an incredible ability to adjust focus, allowing us to see objects clearly at different distances. This process, known as accommodation, involves the contraction and relaxation of the ciliary muscles in the eye, which change the shape of the lens to focus light onto the retina.
In conclusion, the abducens nerve (CN VI) plays a crucial role in eye movement by innervating the lateral rectus muscle, allowing for outward eye movement. Dysfunction of this nerve can lead to abducens nerve palsy, affecting eye coordination and visual function. However, it is important to recognize that eye movement and vision are not solely dependent on this one nerve. They involve a complex interplay of muscles, nerves, and cognitive processing.
If you are experiencing any symptoms or have concerns about your eye health, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who can provide a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate treatment options. Understanding the anatomy, science, and potential health implications of the abducens nerve’s innervation of the eye muscles can help us appreciate the intricate processes involved in vision and the importance of maintaining eye health.
Leave a Reply