The abducens nerve, also known as cranial nerve VI, is a critical component of the human nervous system. Understanding its anatomy, function, and involvement in various disorders is crucial for medical professionals and individuals seeking comprehensive knowledge about this intricate neural pathway. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the abducens nerve, explore the regions it innervates, discuss related disorders, and highlight recent advancements in research and potential future innovations.
Understanding the Abducens Nerve
At the core of comprehending the role of the abducens nerve lies an understanding of its anatomy and function. Let us begin by examining the intricate details that constitute this vital neural pathway.
The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, is a crucial component of the human nervous system. It is responsible for the intricate process of eye movement, specifically the lateral movement of the eye, known as abduction. This means that it plays a pivotal role in our ability to direct our gaze laterally, allowing us to explore our visual environment with precision.
Anatomy of the Abducens Nerve
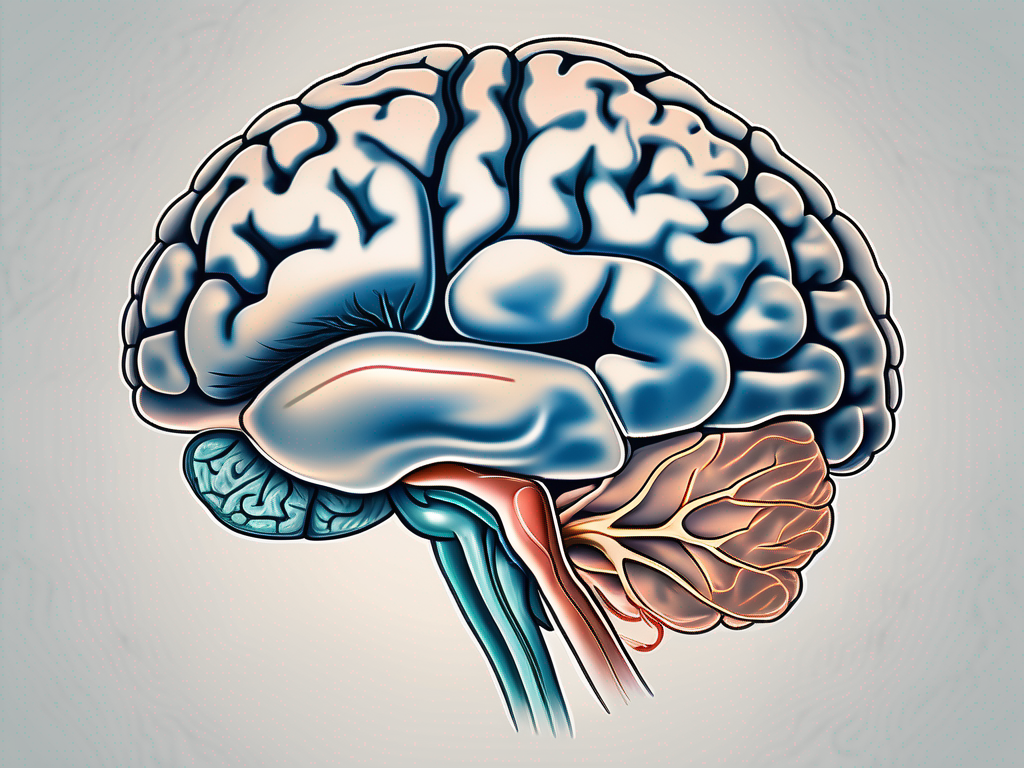
The abducens nerve arises from the pons, a region located in the brainstem. The pons, derived from the Latin word for “bridge,” serves as a vital connection between various regions of the brain. Within the pons, the abducens nerve nucleus orchestrates the movement of the nerve fibers, which eventually emerge from the brainstem and extend towards their respective target muscles.
As the nerve fibers leave the brainstem, they travel through the cavernous sinus, a complex network of veins located at the base of the skull. This intricate pathway ensures the protection and proper functioning of the abducens nerve.
Upon reaching their destination, the nerve fibers innervate the lateral rectus muscle, one of the six extraocular muscles responsible for eye movement. The lateral rectus muscle, as the name suggests, is situated on the outer side of the eye. When the abducens nerve stimulates this muscle, it contracts, causing the eye to rotate outward.
Function of the Abducens Nerve
The primary function of the abducens nerve is to facilitate lateral movement of the eye, specifically abduction. This means that it is responsible for the outward rotation of the eye, enabling us to direct our gaze laterally. The coordinated action of the abducens nerve and associated eye muscles allows us to explore our visual environment with precision.
Eye movement is a complex process that involves the coordinated action of multiple cranial nerves and muscles. The abducens nerve works in conjunction with other ocular motor nerves, such as the oculomotor nerve and the trochlear nerve, to ensure smooth and accurate eye movements.
Disorders affecting the abducens nerve can lead to various eye movement abnormalities. One such condition is abducens nerve palsy, characterized by weakness or paralysis of the lateral rectus muscle. This can result in a decreased ability to move the affected eye laterally, leading to double vision and difficulty focusing on objects to the side.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the abducens nerve is crucial in the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. Medical professionals, such as neurologists and ophthalmologists, rely on this knowledge to assess and manage conditions that affect the abducens nerve.
Regions Innervated by the Abducens Nerve
Moving forward, let us explore the regions innervated by the abducens nerve. By understanding the extensive reach of this nerve, we can comprehend its profound impact on our visual capabilities and overall ocular functionality.
The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in controlling eye movement. It innervates several important structures within the eye, allowing for the precise coordination required for optimal vision.
Innervation of the Eye Muscles
The abducens nerve innervates the lateral rectus muscle, one of the six extraocular muscles responsible for controlling eye movement. The lateral rectus muscle ensures the abduction of the eye as mentioned earlier, allowing us to direct our gaze away from the midline. This elegant coordination between the abducens nerve and the lateral rectus muscle grants us the ability to explore our surroundings without restriction.
Additionally, the abducens nerve also provides innervation to the superior rectus muscle, which is responsible for elevating the eye, and the inferior oblique muscle, which aids in eye elevation and extorsion. These intricate connections between the abducens nerve and these eye muscles allow for a wide range of eye movements, enabling us to look up, down, and diagonally.
Role in Eye Movement
Beyond the lateral rectus muscle, the abducens nerve collaborates with other cranial nerves and eye muscles to orchestrate intricate eye movements. Together, these ocular structures enable essential functions such as convergence, where both eyes come together to focus on nearby objects, and pursuit movements, which track moving objects smoothly.
In addition to these functions, the abducens nerve also plays a vital role in maintaining eye alignment. It works in conjunction with the oculomotor nerve, which innervates the remaining four extraocular muscles, to ensure that both eyes move in a coordinated manner. This coordination is crucial for binocular vision, depth perception, and the ability to accurately judge distances.
Furthermore, the abducens nerve is involved in the control of saccadic eye movements. These rapid, jerky movements allow us to shift our gaze quickly from one point to another. The abducens nerve works in tandem with other neural pathways to execute these precise eye movements, facilitating our ability to scan our environment efficiently.
In summary, the abducens nerve’s innervation of the lateral rectus muscle and its collaboration with other cranial nerves and eye muscles are essential for various eye movements and visual functions. Its intricate connections and precise control contribute to our ability to explore our surroundings, focus on objects, and maintain proper eye alignment. The abducens nerve truly plays a remarkable role in our visual system, emphasizing the complexity and sophistication of the human body.
Disorders Related to the Abducens Nerve
Although the abducens nerve performs its vital functions with remarkable precision, it is not immune to disorders and dysfunctions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available management options for individuals affected by abducens nerve disorders is essential for offering appropriate care and guidance.
The abducens nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in eye movement. It innervates the lateral rectus muscle, which is responsible for moving the eye outward, away from the nose. When the abducens nerve is affected by disorders, it can lead to a range of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s vision and quality of life.
Causes of Abducens Nerve Palsy
Abducens nerve palsy, a condition characterized by impaired eye movement, can manifest due to various factors. These may include neurological causes such as trauma, tumors, vascular issues, and infections. Trauma to the head or eye socket can damage the abducens nerve, leading to paralysis or weakness of the lateral rectus muscle.
Tumors, both benign and malignant, can also exert pressure on the abducens nerve, disrupting its normal function. Vascular issues, such as aneurysms or blood clots, can impede blood flow to the nerve, causing it to malfunction. Infections, such as meningitis or sinusitis, can also affect the abducens nerve and result in palsy.
Identifying the underlying cause is vital for determining the most appropriate course of treatment and management. In some cases, the cause may be reversible, such as in the case of infections, where appropriate antibiotics can help resolve the issue. However, in other cases, such as tumors or trauma, more extensive interventions may be necessary.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Abducens Nerve Disorders
Individuals experiencing abducens nerve disorders may present distinct symptoms, including double vision (diplopia), misalignment of the eyes (strabismus), limited lateral eye movement, and difficulty focusing. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s ability to perform daily activities, such as reading, driving, or even walking.
Accurate diagnosis of abducens nerve disorders typically involves a comprehensive examination by a qualified healthcare professional. The healthcare provider will assess the patient’s medical history, perform a thorough physical examination, and may order additional tests, such as imaging studies or nerve conduction studies, to evaluate the function of the abducens nerve.
It is crucial to emphasize that if you or someone you know is experiencing any concerning symptoms related to the abducens nerve or eye movement, it is imperative to seek medical advice. Only a healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and guidance tailored to individual circumstances.
Once a diagnosis is made, the healthcare provider will work with the patient to develop a management plan. Treatment options for abducens nerve disorders may include medication to address underlying causes, such as antibiotics for infections or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct structural issues or remove tumors that are affecting the nerve.
Additionally, individuals with abducens nerve disorders may benefit from vision therapy or rehabilitation programs aimed at improving eye coordination and function. These programs often involve exercises and techniques designed to strengthen the eye muscles and improve overall visual abilities.
Supportive care and lifestyle modifications can also play a significant role in managing abducens nerve disorders. This may include wearing corrective lenses or using prisms to alleviate double vision, using eye patches or special glasses to help with eye alignment, and practicing good eye hygiene to prevent infections or further complications.
In conclusion, abducens nerve disorders can have a profound impact on a person’s vision and daily life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available management options is crucial for providing appropriate care and support to individuals affected by these conditions. By seeking timely medical advice and following a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with abducens nerve disorders can improve their quality of life and regain visual function.
Treatment and Management of Abducens Nerve Disorders
Effective management of abducens nerve disorders involves a multidimensional approach that addresses both the underlying cause and the symptoms experienced. Various medical interventions and rehabilitation options exist to support individuals affected by these conditions.
When it comes to medical interventions for abducens nerve disorders, there are several treatment options available. One common approach is the use of targeted medications. These medications are designed to specifically target the underlying cause of the disorder, whether it be inflammation, infection, or another issue. By addressing the root cause, these medications can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to treat abducens nerve disorders. These procedures can range from relatively minor interventions to more complex surgeries, depending on the severity of the condition. Surgical options may include nerve decompression, muscle repositioning, or even nerve grafting in severe cases. The goal of these procedures is to restore optimal functionality and minimize ocular limitations.
However, medical interventions alone are not always sufficient to fully address abducens nerve disorders. Rehabilitation and therapy also play a crucial role in supporting individuals affected by these conditions. Qualified professionals, such as physical therapists or occupational therapists, can guide patients through exercises that enhance eye coordination, retrain visual pathways, and optimize visual functionality.
Rehabilitation and therapy options for abducens nerve disorders can vary depending on the individual’s specific needs and goals. Some common techniques include eye exercises, visual tracking exercises, and balance training. These exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles and nerves involved in eye movement, improve coordination, and enhance overall visual function.
In addition to exercises, other therapy options may include the use of specialized equipment or devices. For example, prism glasses can be used to help correct double vision, while eye patches or occlusion therapy may be used to strengthen the affected eye and improve visual alignment.
Furthermore, cognitive and behavioral therapy can also be beneficial for individuals with abducens nerve disorders. These therapies can help address any emotional or psychological challenges that may arise as a result of the condition. By providing support and coping strategies, cognitive and behavioral therapy can improve overall well-being and quality of life.
Overall, the treatment and management of abducens nerve disorders require a comprehensive approach that combines medical interventions, rehabilitation, and therapy. By addressing both the underlying cause and the symptoms, individuals affected by these conditions can achieve improved functionality and a better quality of life.
Future Research on the Abducens Nerve
The advancements in neurological understanding and potential innovations in treatment for abducens nerve disorders are areas of significant interest among researchers and healthcare professionals. Ongoing studies and breakthroughs hold the promise of improving diagnosis, management, and overall outcomes for individuals affected by these conditions.
Advances in Neurological Understanding
Through continued research, advancements in imaging technology, and collaborations between experts in neurology and ophthalmology, our understanding of the abducens nerve and its intricacies is expanding. These developments contribute to enhanced diagnostic capabilities, targeted treatment approaches, and improved patient care.
One area of research that shows promise is the use of advanced imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), to visualize the abducens nerve in greater detail. These imaging modalities allow researchers to study the nerve’s structure and connectivity, providing valuable insights into its function and potential abnormalities.
Furthermore, advancements in neurophysiological techniques, such as electroencephalography (EEG) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), are helping researchers investigate the neural activity associated with the abducens nerve. By studying the electrical signals and magnetic fields generated by the nerve, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of its role in eye movement and coordination.
Potential Innovations in Treatment
Emerging technologies and innovative treatment approaches are continuously being explored to address abducens nerve disorders effectively. Potential innovations may involve novel surgical techniques, wearable devices that aid eye coordination, or advancements in pharmaceutical therapies. These advancements hold immense promise for individuals seeking improved quality of life and visual functioning.
One area of research that is gaining traction is the development of minimally invasive surgical techniques for abducens nerve disorders. These procedures aim to reduce the risk of complications and improve patient recovery time. Researchers are exploring the use of robotic-assisted surgery and microsurgical tools to perform precise interventions on the abducens nerve, minimizing tissue damage and optimizing outcomes.
Another avenue of exploration is the development of wearable devices that can assist individuals with abducens nerve disorders in coordinating their eye movements. These devices may utilize sensors and feedback mechanisms to provide real-time guidance and feedback, helping individuals improve their eye coordination and regain visual functionality.
Additionally, advancements in pharmaceutical therapies are being investigated to target specific abnormalities or deficiencies associated with abducens nerve disorders. Researchers are exploring the potential of gene therapy, neuroprotective agents, and regenerative medicine approaches to restore or enhance the function of the abducens nerve.
In conclusion, the abducens nerve is a remarkable neural pathway that orchestrates lateral eye movement and enables us to explore our surroundings with precision. Its role in ocular functionality and its association with various disorders necessitate deeper understanding and effective management. As ongoing research continues to shed light on the intricacies of this essential nerve, individuals affected by abducens nerve disorders can look forward to potential advancements that enhance their visual capabilities and overall well-being.
Leave a Reply