Cranial nerves play a crucial role in the functioning of our nervous system. Among these, cranial nerve VI, commonly known as the abducens nerve, stands out due to its fascinating name and significant contributions to our overall health. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of cranial nerve VI, including its function, anatomy, and the intriguing reasons behind its name.
Understanding the Basics of Cranial Nerves
The human body is an intricate system of interconnected parts, all working together seamlessly to maintain our well-being. Cranial nerves are a vital component of this complex network, assisting in the transmission of signals between the brain and different parts of the body. These twelve pairs of cranial nerves are responsible for controlling our senses, motor functions, and other essential bodily processes.
But what exactly do these cranial nerves do? Let’s delve deeper into their role and function.
The Role and Function of Cranial Nerves
Cranial nerves serve a myriad of functions, each with its own specific role. They play a significant part in our ability to see, hear, taste, smell, and even control facial movements. For example, the optic nerve (cranial nerve II) is responsible for transmitting visual information from the eyes to the brain, allowing us to perceive the world around us. Similarly, the vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII) enables us to hear and maintain our sense of balance.
But cranial nerves are not limited to sensory functions alone. They also play a crucial role in motor functions. The facial nerve (cranial nerve VII), for instance, controls the muscles of facial expression, allowing us to smile, frown, and make various facial expressions. Another example is the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII), which innervates the muscles of the tongue, enabling us to speak and swallow.
Furthermore, some cranial nerves are essential for maintaining balance and regulating blood pressure. The glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX), for instance, helps regulate blood pressure by monitoring oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood. It also plays a role in the sensation of taste at the back of the tongue.
Without these nerves, our body’s communication and coordination would be severely compromised. They are the messengers that ensure our brain and body can effectively communicate and respond to the world around us.
The Anatomy of Cranial Nerves
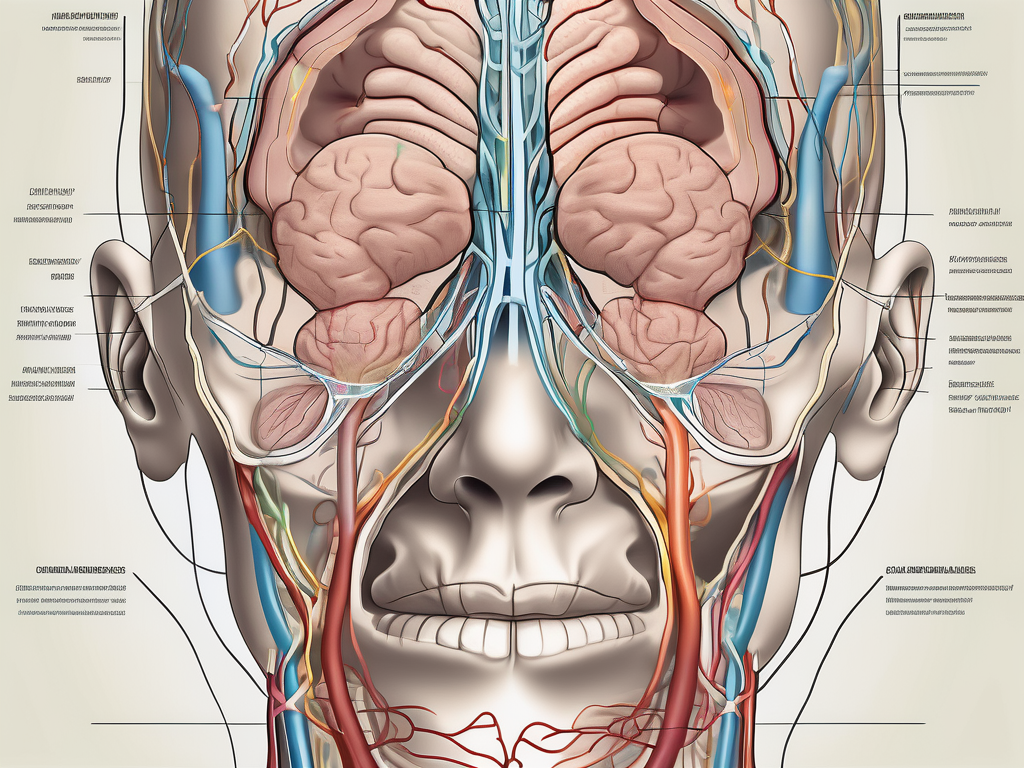
Examining the structure of cranial nerves reveals their intricate arrangement. These nerves originate from the brainstem, a vital part of the central nervous system, and extend throughout the head and neck region. Each cranial nerve has a unique path, supplying different regions of the face, neck, and various sensory organs.
Let’s take a closer look at the anatomy of a few cranial nerves:
1. The olfactory nerve (cranial nerve I) is responsible for our sense of smell. It extends from the olfactory epithelium in the nasal cavity to the olfactory bulb in the brain, allowing us to detect and differentiate various scents.
2. The trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V) is the largest cranial nerve and has both sensory and motor functions. It supplies sensation to the face, including touch, pain, and temperature, and also controls the muscles involved in chewing.
3. The vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) is a complex cranial nerve that innervates multiple organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavities. It plays a crucial role in regulating heart rate, digestion, and even influencing our emotional state.
The detailed anatomy of cranial nerves allows them to target specific areas and fulfill their designated functions effectively. Understanding their pathways and connections is essential for diagnosing and treating various neurological conditions.
The Specifics of Cranial Nerve VI
Now that we have gained a fundamental understanding of cranial nerves, let’s delve into the specifics of cranial nerve VI, the abducens nerve.
The abducens nerve, also known as cranial nerve VI, plays a crucial role in the intricate network of cranial nerves that control various functions of the human body. This particular nerve is responsible for the lateral rectus muscle’s innervation, a small but powerful muscle that controls the sideways movement of the eyeball. Without the proper functioning of cranial nerve VI, our ability to look to the side with precision and accuracy would be compromised.
The Location and Structure of Cranial Nerve VI
Cranial nerve VI is situated in the brainstem, emanating from the pons, a vital part of the brain. The pons, located between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata, serves as a bridge connecting different parts of the brain. It is within this intricate network of neural pathways that cranial nerve VI finds its origin.
From its origin in the pons, cranial nerve VI takes a remarkable path, extending towards the eye. It travels through the cavernous sinus, a complex structure located behind the eye socket, and eventually reaches its destination, the lateral rectus muscle of the eye. This muscle, as mentioned earlier, exclusively controls the sideways movement of the eyeball, allowing us to look to the side with precision and ease.
The Function of Cranial Nerve VI in the Body
The primary function of the abducens nerve is to control the lateral rectus muscle’s contraction, enabling the outward movement of the eye. This seemingly simple action is of utmost importance in our daily lives, as it allows us to explore our surroundings and engage with the world around us.
By coordinating with other cranial nerves, cranial nerve VI ensures both eyes work together harmoniously to achieve synchronized vision. This coordination is essential for depth perception, allowing us to accurately judge distances and perceive the three-dimensional nature of our environment. Additionally, cranial nerve VI plays a vital role in maintaining visual focus, especially when tracking moving objects. Without the proper functioning of this nerve, our ability to visually track objects in motion would be compromised, leading to difficulties in activities such as playing sports or driving.
It is worth noting that cranial nerve VI is susceptible to various disorders and injuries that can disrupt its normal functioning. Conditions such as sixth nerve palsy, which is characterized by the inability to move the affected eye laterally, can result in double vision and difficulties in daily activities. Treatment for such conditions often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including medication, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
In conclusion, cranial nerve VI, the abducens nerve, is a vital component of the complex network of cranial nerves that control the movement and coordination of our eyes. Its role in controlling the lateral rectus muscle allows us to explore our surroundings, perceive depth, and maintain visual focus. Understanding the specifics of cranial nerve VI provides us with a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that enable us to interact with the world through our sense of sight.
The Origin of the Name ‘Abducens Nerve’
Curiously, the abducens nerve derives its name from Latin roots that reflect its unique role and function within the human body. Let’s explore the etymology behind this intriguing name.
The Latin Roots of ‘Abducens’
The term ‘abducens’ finds its origins in the Latin word ‘abducere,’ which translates to ‘to lead away.’ This name aptly describes the nerve’s ability to lead the eye away from the midline, allowing for lateral movement.
As we delve deeper into the Latin roots, it is fascinating to note that ‘abducere’ is a combination of two words: ‘ab,’ meaning ‘away,’ and ‘ducere,’ meaning ‘to lead.’ This combination perfectly encapsulates the nerve’s function of leading the eye away from the central point.
Furthermore, the Latin language has always been known for its precision and descriptive nature. By naming this nerve ‘abducens,’ the anatomists of the past were able to convey the nerve’s function succinctly and accurately.
The Connection Between the Name and Function
The Latin name ‘abducens’ captures the essence of the nerve’s function, emphasizing its role in leading the eye away from the central point. This alignment between the name and function helps medical professionals and researchers understand and identify the nerve with ease.
When studying the abducens nerve, medical professionals are often reminded of the significance of its name. The Latin roots serve as a constant reminder of the nerve’s purpose, making it easier to comprehend and remember its function within the complex network of the human body.
Moreover, the connection between the name and function of the abducens nerve highlights the meticulousness and attention to detail that anatomists and scientists have exhibited throughout history. By carefully selecting a name that accurately reflects the nerve’s role, they have contributed to the clarity and precision of medical terminology.
In conclusion, the name ‘abducens’ not only has a rich etymology rooted in Latin, but it also serves as a testament to the ingenuity and thoughtfulness of those who named it. The Latin roots ‘abducere’ beautifully capture the nerve’s ability to lead the eye away from the midline, while the connection between the name and function aids in understanding and identification. The abducens nerve stands as a fascinating example of how language and anatomy intertwine, creating a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the human body.
Other Names for Cranial Nerve VI
As with many medical terms, cranial nerve VI, or the abducens nerve, has undergone a rich historical evolution. Alternative names and terms have been used throughout different eras to describe this fascinating nerve.
Historical Names and Terms
In years past, cranial nerve VI has been referred to as the “Sixth Nerve” or “Nervus Sextus” in Latin. These simplistic labels may lack the poetic flair of the term ‘abducens,’ but they serve as testament to the long-standing mystery and intrigue surrounding this crucial nerve.
During the Renaissance period, when anatomical knowledge was rapidly expanding, the abducens nerve was sometimes called the “Nerve of Lateral Rectus” due to its connection to the lateral rectus muscle of the eye. This name highlighted the nerve’s role in controlling the movement of the eye laterally, allowing for smooth and coordinated eye movements.
Interestingly, in ancient Greek medicine, the abducens nerve was associated with the concept of “ophthalmos,” which referred to the eye. This association led to the nerve being called the “Ophthalmic Nerve” in some medical texts of that time. This name emphasized the nerve’s importance in eye function and its connection to visual perception.
Modern Medical Terminology
With advancements in medical knowledge, modern terminology has expanded to encompass more detailed nomenclature. Professionals frequently employ the specific term ‘cranial nerve VI’ or ‘abducens nerve’ to accurately denote this unique neural pathway.
The term ‘abducens’ itself is derived from the Latin word “abducere,” which means “to lead away.” This name reflects the nerve’s primary function of innervating the lateral rectus muscle, which is responsible for abducting or moving the eye away from the midline.
In addition to these specific names, the abducens nerve is also referred to as a “motor nerve” due to its role in controlling the movement of the eye. This distinction sets it apart from other cranial nerves that may have sensory or mixed functions.
Furthermore, the abducens nerve is part of the larger cranial nerve system, which consists of twelve pairs of nerves that originate from the brain. Each cranial nerve has a specific function and innervates different structures in the head and neck region. Understanding the intricate network of cranial nerves is crucial for diagnosing and treating various neurological conditions.
Overall, the various names and terms associated with cranial nerve VI highlight the historical, anatomical, and functional aspects of this remarkable nerve. From its simple beginnings as the “Sixth Nerve” to its modern designation as the abducens nerve, this neural pathway continues to captivate medical professionals and researchers alike.
The Clinical Importance of Cranial Nerve VI
Beyond linguistic and anatomical significance, cranial nerve VI holds substantial clinical importance in the medical field. Understanding the disorders associated with this nerve and its role in diagnosis and treatment is crucial for healthcare professionals.
Disorders Associated with Cranial Nerve VI
Disruptions to the abducens nerve can result in a range of health conditions. Some individuals may experience strabismus, a condition characterized by misalignment of the eyes. This misalignment can manifest as an inward or outward deviation, compromising visual coordination. Strabismus can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life, affecting their ability to perform tasks that require depth perception, such as driving or playing sports.
In addition to strabismus, other conditions such as nerve palsy or tumors can also affect the normal functioning of cranial nerve VI. Nerve palsy occurs when there is damage or inflammation of the abducens nerve, leading to weakness or paralysis of the muscles that control eye movement. This can result in double vision, difficulty focusing, and limited eye mobility. Tumors, on the other hand, can exert pressure on the abducens nerve, causing similar symptoms and potentially affecting other nearby structures.
The Role of Cranial Nerve VI in Diagnosis and Treatment
When evaluating patients with eye-related issues, healthcare practitioners consider the functioning of cranial nerve VI in their diagnostic process. By performing precise examinations and assessing eye movements, medical professionals can identify potential abnormalities associated with this nerve. They may use techniques such as the Hirschberg test, which involves shining a light into the patient’s eyes to observe the position of the reflection, to assess eye alignment.
Once a diagnosis is made, treatment options may vary depending on the specific condition diagnosed. In cases of strabismus, non-surgical interventions such as vision therapy or the use of prism glasses may be recommended to help align the eyes and improve coordination. However, in more severe cases or when the underlying cause is a tumor or nerve palsy, surgical interventions may be necessary. Surgical procedures can involve realigning the eye muscles or removing the tumor to relieve pressure on the abducens nerve.
It is important to note that the treatment approach for disorders associated with cranial nerve VI is highly individualized, taking into account factors such as the patient’s age, overall health, and the severity of the condition. Regular follow-up appointments and ongoing monitoring are often necessary to ensure the effectiveness of the chosen treatment and to address any potential complications that may arise.
In conclusion, cranial nerve VI, or the abducens nerve, plays a significant role in our visual coordination and eye movements. Its name, derived from Latin roots, eloquently reflects its function within the human body. As with any medical concern, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and guidance. Understanding the fascinating intricacies of our cranial nerves not only deepens our appreciation for the human body but also empowers us to prioritize our overall well-being.
Leave a Reply